General Restorative Dentistry
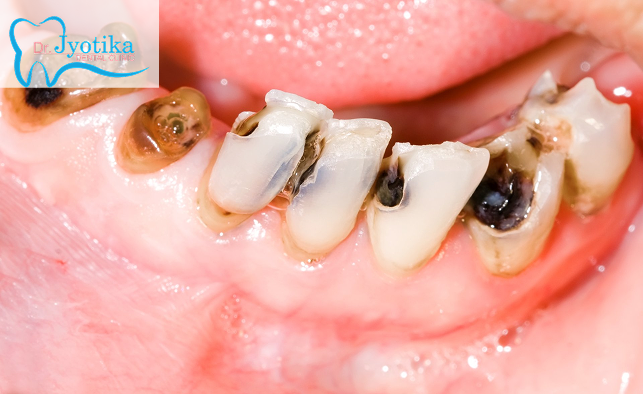
Cavities and cracks can damage tooth structure, requiring restorative treatment—from a simple filling to a full crown. Understanding what causes cavities and how to prevent them is key to maintaining long-term dental health.
What Is a Cavity?
Teeth are hard, calcified tissues, but they can erode when exposed to acids. Acid can penetrate the enamel (the tooth’s outer layer), reach the dentin (the inner layer), and eventually affect the pulp (the soft core containing nerves and blood vessels). This progressive damage is what we call a cavity.
Cavities often form due to:
- Acid produced by oral bacteria feeding on sugar and sticky foods
- Frequent consumption of carbonated beverages, candies, and acidic drinks
Preventing Cavities
- Brush gently but thoroughly with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to clean between teeth
- Limit sugary, sticky, and acidic foods and drinks
- Regular dental checkups and cleanings
Fluoride in toothpaste, rinses, and some drinking water strengthens enamel, helping protect teeth from decay.
Why Dentists Sometimes “Watch” a Cavity
If a cavity is limited to the enamel, it may be monitored instead of treated immediately. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene can prevent it from worsening. Once it reaches the softer dentin layer, treatment is necessary to avoid more extensive damage.
Why Cavities Can Be Painless
Many cavities do not cause pain until they reach the tooth’s nerve. That’s why regular checkups are essential—early detection allows us to restore teeth with minimal treatment before they become painful or require more complex procedures, like root canals.
Why Teeth Break
Teeth can chip or fracture over time due to chewing forces, existing cavities, or habits like grinding and clenching. This is normal wear and tear and does not mean your teeth are weak.
Restorative Options at Jyotika Dental
Our team uses modern, conservative techniques to repair and restore teeth:
- Tooth-Colored Fillings: Repair minor cavities and damage
- Inlays and Onlays: Restore more extensive damage while preserving tooth structure
- Crowns (Caps): Protect severely decayed or damaged teeth
- Bridges: Replace missing teeth when implants are not an option
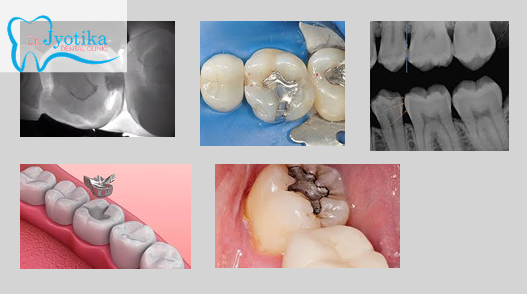
Explore our Smile Gallery to see examples of restorative dentistry and the transformative results we achieve.

